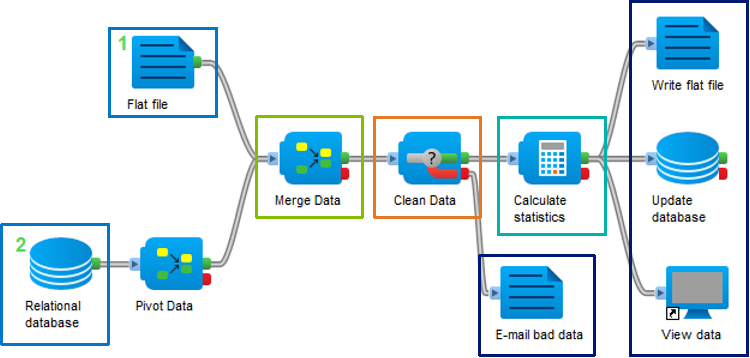
µTS_显微镜/扫描电镜原位加载系统
“Meso is the new nano.” - Prof.Peter Hosemann, UC Berkeley

µTS – Meso Scale Under Microscope Universal Load Frame
显微镜下的介观尺度万能加载系统
Psylotech公司的μTS是一个独特的介于纳米压头和宏观万能加载系统之间尺度的微型万能材料试验系统,可通过数字图像相关软件(DIC)和显微镜相结合的非接触式测量来获取局部的应变场数据。
Psylotech’s µTS is a miniature universal material test system uniquely capable on length scales between nano-indenters and macro universal load frames. Non-contact, local strain measurement on these so-called meso length scales comes from digital image correlation (DIC) and microscopy.
技术说明 Technology
μTS对长度,速度和力在多种尺度下具有独特的适应性:
• 长度:尽管光学显微镜具有景深限制,μTS系统可通过有效的约束试件加载过程中的离面运动,来保证高放大倍率下的数字图像相关性分析。
• 速度:高精度执行器直接驱动滚珠丝杠,使速度可调范围跨越了9个数量级。 既可在高速实现有效的负载控制,也可用于速率相关研究以及蠕变或应力松弛试验。
• 力:专有的超高分辨率传感器技术,相比应变计,分辨率提高了100倍。
The µTS uniquely accommodates multiple scales in length, speed and force.
• Length: Constraining out-of-plane motion, the µTS enables effective high magnification digital image correlation, despite depth-of-field limitations in the optical microscopes.
• Speed: The direct-drive ballscrew actuator enables speeds covering 9 orders of magnitude. High speed enables effective load control, rate dependent studies and creep or stress relaxation tests.
• Force: Proprietary ultra high resolution sensor technology provides 100x higher resolution compared to strain gaged alternatives.
即刻下载并查阅µTS产品彩页 Download µTS Brochure (2018.09.06更新版).
夹具 Grips
 | 作为通用测试系统,μTS为不同类型的夹具配备了T型槽接口。 三角形/平面界面几何形状确保精确的旋转对齐。可用的标准夹具包括拉伸、压缩、梁弯曲和混合模式Arcan。 并可根据您的特定需求设计定制夹具。 As a universal test system, the µTS implements a T-slot interface for different kinds of grips. The triangle/flat interface geometry ensures accurate rotational alignment. Available standard grips include tension, compression, beam bending and mixed-mode Arcan. Ask us how custom grips can be designed for your specific needs. |
 | 环绕拉伸 在其顶部和底部表面上夹紧试件可能导致在加载期间的离面运动。 环绕拉伸夹具可将样品保持在垂直于观察平面的表面上,并且有效地将样品保持在平面内。 另外一个好处是,样品可以非常快速地安装在环绕式夹具中。 Clamping a specimen on its top and bottom surfaces can lead to out of plane motion during loading. The wrap around tension grips hold the sample on surfaces perpendicular to the observation plane and have been effective in keeping the specimen in plane. As an added benefit, specimens can be very quickly mounted in the wrap around grips. |  | 夹钳拉伸 Some materials, like film or chopped fiber composites, are not conducive to the wrap-around grip geometry. Clamping grips can be used in these cases. A vertical micrometer screw adjustment can compensate causes out of plane motion. Also, a single clamping screw eliminates asymmetric clamping torque. |
| Arcan 拉剪混合 Arcan夹具的几何结构设计可支持单轴加载框架下的拉剪混合模式加载。通过旋转调整夹具锁定销钉位置,可调控纯剪切应变与纯轴向应变的比例。该技术可充分利用数字图像相关法实现局部应变测量。 The Arcan grip geometry enables mixed-mode loading from a uniaxial load frame. Rotating the grips controls the ratio of pure shear to pure axial strain. This technique takes full advantage of local strain measurement via digital image correlation. |  | Compression 压缩 平面压缩夹具采用轻型弹簧托架承载样品,在施加载荷前保持样品稳定。受力时,轻型弹簧可轻松随试样膨胀而变形。 The compression platens implement a lightly sprung shelf to hold the sample before load is applied. Under load, the light spring easily deforms as the specimen expands |  |
 | Beam bending 梁弯曲 系统可提供三点和四点弯曲夹具。除一个接触点外,其余均位于淬火钢辊上。固定接触点可防止位移,避免在利用挠度监测裂纹扩展时产生虚假挠度读数。三点与四点弯夹具均采用与平面压缩夹具相同的轻型弹簧托架。 Three and Four point bending fixtures are available. All but one contact point is on a hardened steel roller. The fixed contact point prevents translation, which can give false compliance readings when using compliance to monitor crack growth. Both 3- and 4-point fixtures implement the same lightly sprung shelf as the compression platens. |  |
可选配置 Optional
µTS的模块化设计兼具灵活性与强大功能。以下是部分常规可选配置项:
低力值称重传感器:1.6千牛称重传感器的100牛顿版本可提供更精细的力值分辨率。如需100纳牛顿级别的力值分辨率,请垂询。
提升速度:采用高螺距滚珠丝杠、增加电机绕组层数或提高输入电压,可将速度从标准系统的80毫米/秒提升至最高250毫米/秒。
行程扩展:标准系统的40毫米行程可根据实验需求大幅增加。
环境箱:通过选配不同的温度环境箱可实现-100℃至350℃至高于1200℃的温度控制,更高温度亦可定制。低温环境需使用液氮。
扫描电子显微镜(SEM):µTS可进行真空硬化处理以适配扫描电子显微镜。需注意:扫描时间及时空漂移会影响SEM图像的DIC分析效果,需要具有漂移几何的DIC软件修正该偏差,而光学显微镜不存在此限制。
自动伺服对中平台:X-Stage辅助对中定位平台可确保样品观测区始终保持在显微镜视野内,不受变形程度影响。
简化版位移传感器:为降低成本,也可利用旋转编码器和滚珠丝杠节距推算位移,替代高分辨率局部位移传感器。
亚10纳米定位精度:电机搭载22位旋转编码器,配合1毫米螺距滚珠丝杠可实现约238皮米线性分辨率。结合传感器噪声与调谐抖动补偿,闭环系统线性误差可控制在10纳米以内。
完整交钥匙方案:Psylotech方案可包含全套DIC系统,包含奥林巴斯BXFM悬臂式显微镜、Correlated Solutions VIC-2D数字图像相关软件、隔振台及不同分辨率的高像素相机。
共聚焦拉曼显微镜:Psylotech的µTS系统已集成至Witec共聚焦拉曼显微镜。Psylotest控制软件可驱动显微镜载物台实现样品居中定位。
拉-扭执行器:载荷框架可选配力-扭矩传感器及额外扭力电机,可实现拉-扭双向复合加载。
The modularity of the µTS is as flexible as it is powerful. Below are some of the easily configured options.
Low Force Load Cell: 100N version of the 1.6 kN load cell provides finer force resolution. Ask us about force resolution down to 100 nano Newtons.
Increased Speed: A higher pitch ball-screw, increased motor stack, or higher input voltage can produce speeds up to 250 mm/sec, up from the 80 mm/sec of the stock system.
Extended Stoke: The 40mm stock instrument stroke can be extended substantially, depending on experimental need.
Environmental Chamber: Temperatures between -100C and 200C can be controlled via the optional environmental chamber. Higher temperatures are also available. Low temperatures require liquid nitrogen.
SEM: The µTS can be vacuum hardened for use in scanning electron microscopes. Please note, rastering time as well as spacial and temporal drift complicate DIC with SEM images. Optical microscopy does not have these limitations.
Centering X-stage: A secondary positioning stage keeps any specimen inside the microscope field of view, regardless of the amount of deformation.
Samplified Displacement Sensor: As a cost saving measure, the rotary encoder and ball screw pitch can be used to infer displacements in lieu of the high resolution local displacement sensor.
Sub-10nm Positioning: With a 22 bit rotary encoder mounted to the motor, a 1mm pitch ball screw gives ~238 picometers of linear resolution. Noise of the sensor and tuning jitter bring the closed loop error to under 10nm linearly.
Complete Turnkey Package: Psylotech can provide a complete DIC package, including an Olympus BXFM boom-mounted microscope, Correlated Solutions Vic2D software, a vibration isolation table and a 4 MP USB3.0 camera.
Confocal Raman Microscope: Psylotech’s µTS has been integrated into a Witec confocal Raman microscope. The Psylotest control software controls the microscope stage for specimen centering.
Tension-Torsion Actuator: An extra motor is added to the fixed side of the load frame in addition to a force-torque load cell in order to facilitate axial and torsion loading.
独有特性 Differentiation
| µTS系统提供精密的运动控制和极高的精度。作为多功能仪器,它支持多种实验技术。该系统专为实验人员设计,在细节方面精心考量,包括: The µTS offers sophisticated motion control and a high degree of precision. It is a versatile instrument, enabling a broad variety of experimental techniques. Designed for experimentalists, careful attention to details include: |
Dimensions in mm |
| Ball Screw 滚珠丝杠 µTS采用直接驱动滚珠丝杠,而非通过齿轮箱驱动的简单导螺杆。由此可降低摩擦、提升运动控制精度并减少维护需求。此外,相比于导螺杆执行器狭窄的速度范围,直接驱动滚珠丝杠而已提供极宽泛的速度范围。 The µTS incorporates a direct drive ball screw, rather than simple lead screws driven through a gearbox. The result is less friction, improved motion control and less maintenance. Moreover, lead screw actuators are typically limited to a narrow range of speeds. | Psylotest Control Software 控制软件 µTS控制软件采用LabVIEW编写,具备测试段专用的数字滤波功能及集成式相机触发机制,可简化数据与DIC图像数据分析的协同处理。高级用户可选择修改程序以集成外部系统。 The µTS control software is written in LabVIEW. It features test-segment specific digital filtering and integrated camera triggering, simplifying data and DIC image coordination. Advanced users have the option to modify the program to integrate external systems. | |
| Speed 速度 相比于导螺杆系统狭窄的速度范围,直驱滚珠丝杠覆盖了9个数量级的速度范围,既能达到宏观尺寸伺服液压载荷框架的高速运行,也能实现如草木生长般的缓慢移动。高速特性赋予其更广泛的测试适用性,包括: - 速率依赖性研究 - 阶跃荷载测试(如蠕变或应力松弛) - 有效载荷控制 - 疲劳测试 Alternative lead screw systems are typically limited to a narrow range of speeds. The direct drive ballscrew covers 9 orders of magnitude in speed. It can move as fast as a macro sized servohydraulic load frame or as slow as grass growing on a hot summer’s day. High speed enables versatility for more types of testing, including: -Rate dependent studies-Step load tests, such as creep or stress relaxation -Effective load control -Fatigue | Centering Stage 对中平台 在实验过程中,大变形可能导致特定感兴趣区域偏离显微镜视野。左右旋螺钉的对置配置可缓解此问题,但该方案会加剧弯曲样品的居中问题。此外,当感兴趣区域不在样品中心时又该如何处理? µTS系统可配置自动对中平台。该辅助平台的驱动器与主系统驱动器实现从属联动,可实现任意比例的运动。相对十字头运动不再受限于50/50比例,即使是梁弯曲样品也能保持在视野范围内。 Large deformations can cause a specific area of interest to exit the microscope’s field of view during an experiment. Opposing left/right handed screws can mitigate this problem, but such a configuration exacerbates he centering problem for beam bending samples. Also, what happens when the area of interest is not in the center of the sample? The µTS can be configured with a centering stage. The actuator of this secondary stage is slaved to the main system actuator such that any ratio of motion can be achieved. Relative cross-head motion is not tied to 50/50, and even beam bending samples can be maintained within the field of view. | |
| Out-of-plane motion 离面运动控制 在µTS测试系统中,固定十字头、T型槽夹具适配器和负载传感器被集成到由17-4不锈钢(马氏体不锈钢)实心块切削而成的单一部件中。这种集成设计有助于在高倍显微镜放大下实现高质量的原位图像采集。更少的部件消除了公差叠加,进而控制了平面外运动,同时极大简化了系统对齐流程。 为进一步控制平面外位移,双线性导轨对称布置于加载平面。摩擦产生的任何力矩均被平衡抵消,不会引发俯仰或偏航。而早期此类设计通常将线性导轨置于加载平面下方,导致高倍显微镜放大条件下出现聚焦问题。 In the µTS, the fixed cross-head, T-slot grip adapter, and load cell are integrated into a single part cut from a solid block of 17-4. This integration contributes to quality in situ image capture under high microscope magnification. Eliminating tolerance stack-up controls out-of-plane motion. The integration also greatly simplifies the system alignment procedure. To further control out-of-plane motion, dual linear guides are symmetrically placed in the loading plane. Any moments from frictional effects are balanced and do not contribute to pitch or yaw. Previous designs placed linear guides below the loading plane, causing focus problems under high microscope magnification. | Load Cell 载荷传感器 µTS采用专有的Psylotech技术,灵敏度达400 mV/V,而通用载荷框架中常见的应变片式传感器仅为2 mV/V。灵敏度的提升意味着分辨率提高约100倍,可实现多级力值实验。例如,标准1.6kN负载传感器可替代常规16N传感器进行测试。高级用户可利用其高灵敏度开展创新实验,如通过顺应性测量裂纹长度,或在复合材料测试中替代声学传感器。 The µTS leverages proprietary Psylotech technology with 400 mV/V sensitivity compared to 2 mV/V from strain gauged alternatives typically found in universal load frames. The increased sensitivity means about 100x higher resolution, enabling multiple force scale experiments. For example, the stock 1.6 kN load cell can be used on tests where one would normally use a 16 N load cell. Advanced users could leverage this high sensitivity to enable new experiments, such as crack length from compliance or replacing acoustic sensors in composite tests. | |
| Displacement Sensor 位移传感器 µTS系统通过试样轴线监测位移。而其他系统通常采用离轴测量方式,导致实际实验中不可避免的小角度偏移或偏航会产生虚假位移读数。某些情况下,甚至旋转位置和俯仰角也会被用于推断位移。 凭借高分辨率轴向位移传感器,Psylotech基于十字头位移传感器的反馈信号,实现了优于5纳米的闭环位置控制。这种控制技术能够应用于大行程滚珠丝杠执行器,因为反馈传感器在负载传动系统中测量的是丝杠下游的位移。 The µTS monitors displacement on axis with the specimen. Alternative systems implement off-axis measurements, such that small pitch or yaw inevitable in real-world experiments show up as false displacement readings. In certain cases, rotary position and pitch are also used to infer displacement. With the high-resolution on-axis displacement sensor, Psylotech has achieved better than 5 nm closed loop position control based on feedback from the cross-head displacement sensor. Such control is possible from a large stroke ball-screw actuator, because the feedback sensor measures displacement downstream of the screw in the load train. |
演示视频 Video
更多了解µTS测试系统请参阅 See more information: µTS试验系统模块与应用说明
精选已出版文章 Selected Publications
2021
UT Dallas
Runyu Zhang, Huiluo Chen, Sadeq Malakooti, Simon Oman, Bing Wang, Hongbing Lu, Huiyang Luo, Quasi-Static and Dynamic Confined Compressive Behavior of Glass Beads by In-Situ X-Ray Micro-Computed Tomography.
Purdue University
MehdiShishehbor, HyeyoungSon, MdNuruddin, Jeffrey P.Youngblood, ChelseaDavis, Pablo D.Zavattieri, Influence of alignment and microstructure features on the mechanical properties and failure mechanisms of cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) films.
2020
University of Waterloo
Dibakar Mondal, Thomas L Willett, Extrusion Increases the Mechanical Properties of 3D-Printable Nanocomposite Biomaterials.
Clemson University
Shabanisamghabady, Mitra, Dislocation Slip and Deformation Twinning in Face Centered Cubic Low Stacking Fault Energy High Entropy Alloys (2020). All Dissertations. 2756.
Purdue University
Mitchell L. Rencheck, Andrew J. Weiss, Sami M. El Awad Azrak, Endrina S. Forti, Md. Nuruddin,
Jeffrey P. Youngblood, and Chelsea S. Davis*
ACS-Applied Polymer Materials (ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 578−584), Nanocellulose Film Modulus Determination via Buckling Mechanics Approaches
NASA, Marshall Space Flight Center
O Mireles, Z Jones, O Rodriguez, M Ienina – AIAA Propulsion and Energy 2020 Forum, 2020, Development of Additive Manufactured Ultra-Fine Lattice Structures Propulsion Catalyst
NASA, Marshall Space Flight Center
O Mireles, O Rodriguez, Y Gao, N Philips – AIAA Propulsion and Energy 2020 Forum, 2020, Additive Manufacture of Refractory Alloy C103 for Propulsion Applications
University of Utah, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering
Mirmohammad, H., Gunn, T. & Kingstedt, O.T.- Experimental Techniques, 2020. In-Situ Full-Field Strain Measurement at the Sub-grain Scale Using the Scanning Electron Microscope Grid Method.
The Graduate School Seoul National University, Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering
Tomas Webbe Kerekes- Enhancement of Mechanoluminescence Sensitivity of SrAl2O4: Eu2+, Dy3+ Composite by Ultrasonic Curing Method.
University of Waterloo, Dept. of Systems Design Engineering
Dibakar Mondal & Thomas Willett, Mechanical properties of nanocomposite biomaterials improved by extrusion during direct ink writing.
University of Tennessee Knoxville, Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering
Mohmad Moshin Thakur & Dayakar Penumadu, Triaxial compression in sands using FDEM and micro-X-ray computed tomography.
2019
Argonne National Laboratory
X Zhang, M Li, JS Park, P Kenesei, JD Almer, In-situ High-energy X-ray Study of Deformation Mechanisms in Additively Manufactured 316 Stainless Steel.
Argonne National Laboratory
M Li, X Zhang, JD Almer, JS Park, P Kenesei –2019, Final Report on Investigating Grain Dynamics in Irradiated Materials with High-Energy X-rays.
2018
Lawrence Berkeley National Lab / University of California – Berkeley
Raja, S. N., Ye, X., Jones, M. R., Lin, L., Govindjee, S., & Ritchie, R. O. (2018). Microscopic mechanisms of deformation transfer in high dynamic range branched nanoparticle deformation sensors. Nature communications, 9(1), 1155.
Clemson University
Adams, D., & Turner, C. J. (2018). An implicit slicing method for additive manufacturing processes. Virtual and Physical Prototyping, 13(1), 2-7.
U.S. Army Research Lab
Cline, J., Wu, V., & Moy, P. (2018). Assessment of the Tensile Properties for Single Fibers (No. ARL-TR-8299). US Army Research Laboratory Aberdeen Proving Ground United States.
2017
University of California – Berkeley
Gu, X. W., Ye, X., Koshy, D. M., Vachhani, S., Hosemann, P., & Alivisatos, A. P. (2017). Tolerance to structural disorder and tunable mechanical behavior in self-assembled superlattices of polymer-grafted nanocrystals. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 201618508.
Clemson University
Sane, H. (2017). A Holistic Investigation and Implementation of Fluidic Origami Cellular Solid for Morphing and Actuation.
Baikerikar, P. J., & Turner, C. J. (2017, August). Comparison of as-built FEA simulations and experimental results for additively manufactured dogbone geometries. In ASME 2017 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference. American Society of Mechanical Engineers.
U.S. Army Research Lab
Roenbeck, M. R., Sandoz-Rosado, E. J., Cline, J., Wu, V., Moy, P., Afshari, M., Reichert, D., Lustig, S.R., & Strawhecker, K. E. (2017). Probing the internal structures of Kevlar® fibers and their impacts on mechanical performance. Polymer, 128, 200-210.
Cole, D. P., Henry, T. C., Gardea, F., & Haynes, R. A. (2017). Interphase mechanical behavior of carbon fiber reinforced polymer exposed to cyclic loading. Composites Science and Technology, 151, 202-210.
Iowa State University, Ames Laboratory
Tian, L., Russell, A., Riedemann, T., Mueller, S., & Anderson, I. (2017). A deformation-processed Al-matrix/Ca-nanofilamentary composite with low density, high strength, and high conductivity. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 690, 348-354.
Czahor, C. F., Anderson, I. E., Riedemann, T. M., & Russell, A. M. (2017, July). Deformation processed Al/Ca nano-filamentary composite conductors for HVDC applications. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering(Vol. 219, No. 1, p. 012014). IOP Publishing.
University of New Hampshire
Knysh, P., & Korkolis, Y. P. (2017). Identification of the post-necking hardening response of rate-and temperature-dependent metals. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 115, 149-160.
2016
University of New Hampshire
Zhai, J., Luo, T., Gao, X., Graham, S. M., Baral, M., Korkolis, Y. P., & Knudsen, E. (2016). Modeling the ductile damage process in commercially pure titanium. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 91, 26-45.
Ripley, P. W., & Korkolis, Y. P. (2016). Multiaxial deformation apparatus for testing of microtubes under combined axial-force and internal-pressure. Experimental Mechanics, 56(2), 273-286.
配置说明 Configuration
点击上图进入配置说明 For typical configurations, Please click image above.
技术溯源 About
µTS的核心运动控制技术是美国陆军研究实验室WMRD SBIR项目中研发的部分成果。与伊利诺伊大学厄巴纳-香槟分校的Ioannis Chasiotis教授的合作对该项目至关重要。其目标是将Chasiotis团队积累的经验应用于实际,使其更具商业价值且更易于使用。在此过程中,Psylotech公司融入其高分辨率传感器技术,并开发出近纳米级定位滚珠丝杠执行器,最终打造出µTS系统。
在争相探索纳米尺度的科研过程中,人们往往忽略了相差六个数量级的介于10毫米至5纳米之间的“介观”尺度。µTS系统正是利用数字图像相关技术,实现了该尺度范围内局部应变的精准测量。
The core motion control technologies for the µTS were developed in an Army Research Lab WMRD SBIR. Collaboration with Prof. Ioannis Chasiotis at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign was critical to that effort. The goal was to apply lessons learned by the Chasiotis group, making them commercially accessible and more user-friendly. In the process, Psylotech added its high resolution sensor technologies and developed a near-nano scale positioning ball screw actuator to create the µTS.
In the rush to understanding the nano scale, six orders of magnitude in length scale were glossed over. The µTS takes advantage of digital image correlation for local strain measurement on these “meso” length scales between 10 mm and 5 nm.